Connecting to a Database with Visual Studio Tools
Before we delve into the data-driven world of ADO.NET, let’s first take a look at some tools available in the Visual Studio products. The following example shows you one way of connecting to a database without writing any code.
Creating a Connection to a Database
Open Visual C# Express and create a new Windows Forms Application. Name the project as DatabaseConnection. In Visual Studio, the Database Explorer is called Server Explorer. It is opened by default in Visual C# Express located in the left as a tab.
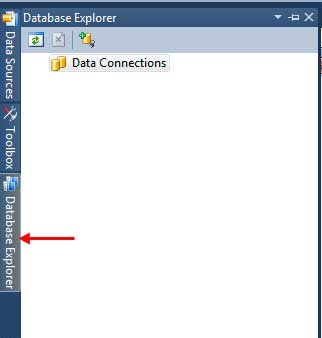
If you can’t find the Database Explorer, go to View > Other Windows > Database Explorer to open it up. Click the Connect to Database icon in the Database/Server Explorer.
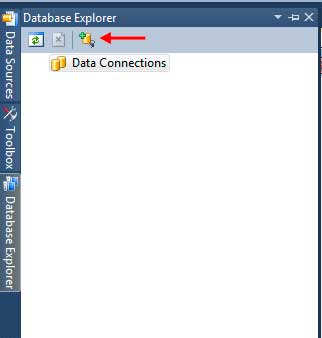
Clicking it shows up the Add Connection Window.
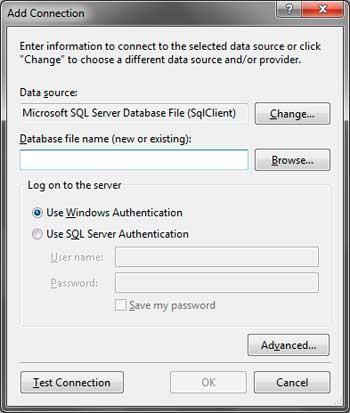
Make certain that the Data source utilizes Microsoft SQL Server Database File. If not, you can click the Change button and choose the appropriate data source. We also need to provide the file name of the database file that was created when we create our database. Click Browse to show up the open dialog. By default, the database files of SQL Server Express is located in C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL.1MSSQLData. Paste this path in the URL bar of the Open dialog to immediately go to that directory. Find the University.mdf file and select it. Click Open.
If an error shows up telling that file is used by another program. Open up the Services program by clicking Start and typing the word services in the search box. Find the SQL Server (SQLEXPRESS) service and right click on it. Choose Restart to restart the service.
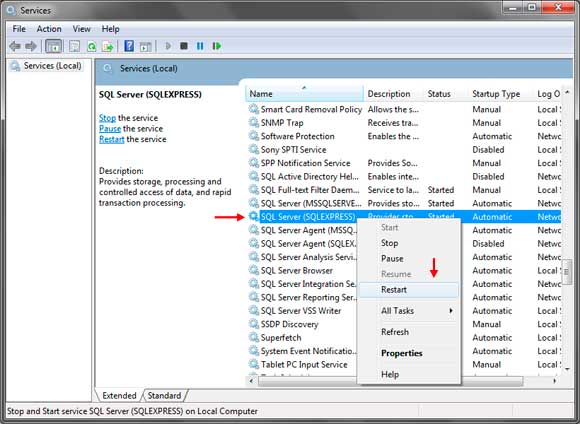
After it is restarted, we can now go back to choosing the University.mdf file. After pressing open, click the Test Connection button in the Add Connection Window to test if our application can successfully connect to the database. If nothing is wrong, then a success message will show up.
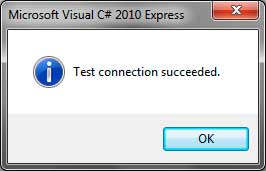
Press OK to close the message. You can also choose the Authentication mode to be used. You can use Windows Authentication or SQL Server Authentication. You must provide the username and password if you are to use SQL Server Authentication mode. Press OK to close the Add Connection Window and add the database file to the Database Explorer window.
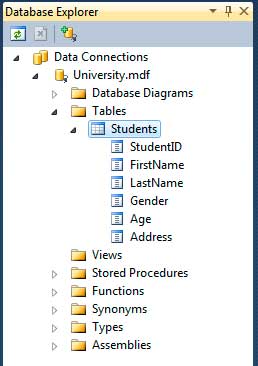
The Database Explorer allows you to see the contents of a database. If you expand a database file such as the University.mdf, you can see parts of it such as its tables and stored procedures. Expanding the Tables node shows our Students table and expanding the table shows its columns.
Creating a DataSet
A DataSet can be considered as a mini database located in the computer’s memory. It’s main purpose is to obtain the data received from the database and store it in different tables just like how a database stores its records. The next step is to create a DataSet that will contain the contents the database that we have connected to. We will be using the Data Sources Window. If you can’t see it, then go to Data > Show Data Sources. It will be located to the left of the IDE by default.
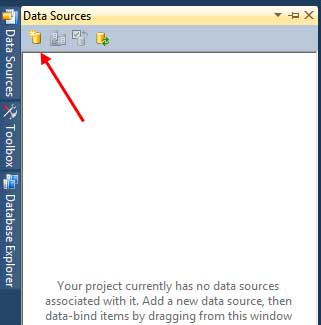
Click the Add New Data Source button to open up the Data Source Configuration Wizard.
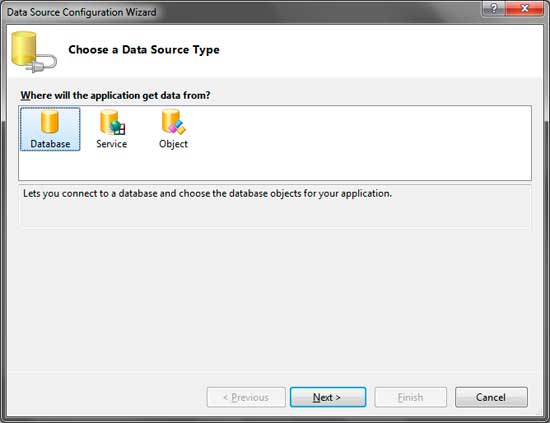
Choose Database and click Next.
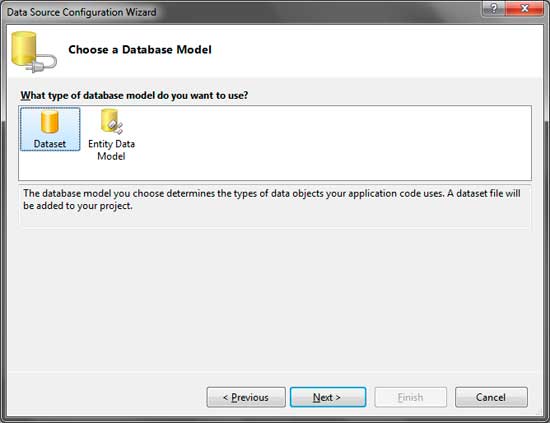
Choose Dataset then click Next.
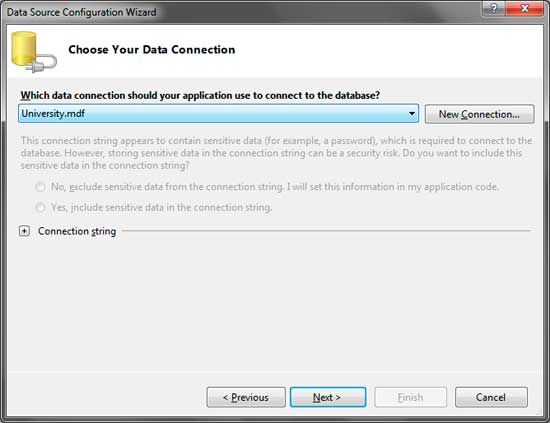
In the combo box, be sure to select University.mdf that we have connected using the Database Explorer. Click Next.
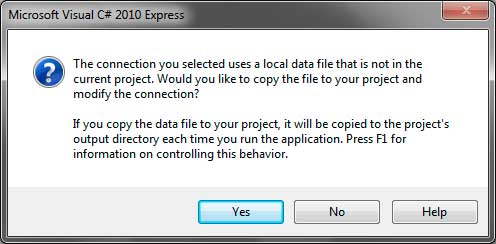
You will then be prompted that the database file needs to be copied to the project’s directory. Clicking yes will copy it to the project’s directory. You can confirm that the database has been copied by looking at the Solution Explorer and finding University.mdf.
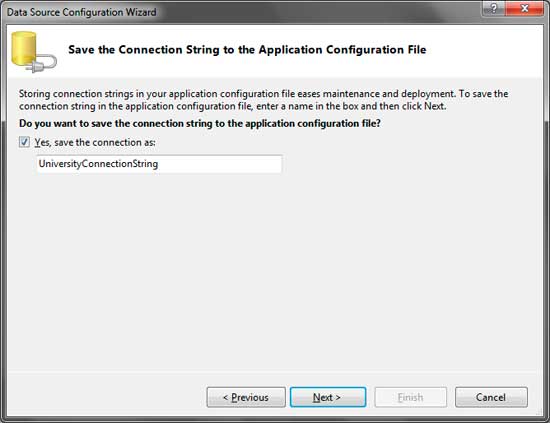
This window simply saves the connection string used to connect to the University database. Connection strings will be discussed in a later lesson. For now, you can leave the defaults and click Next.
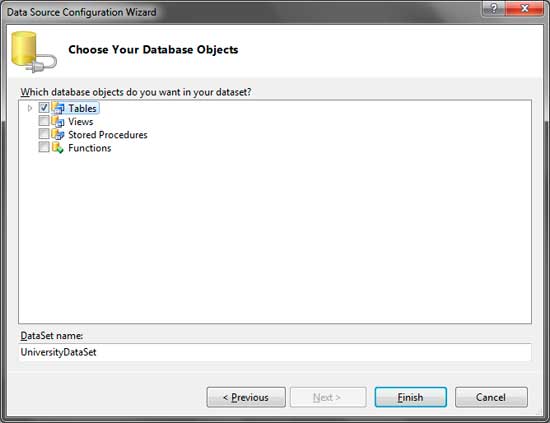
Wait for the Wizard to load the contents of the database. You will then be asked which parts of the database you want to be included in the DataSet. Since we will only be needing the tables, simply check the Tables. The DataSet name specifies the name of the DataSet to be created. Click finish to create the DataSet.
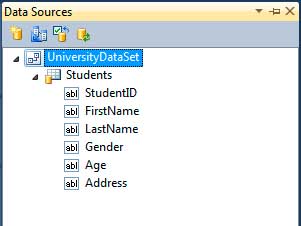
You can now see the created DataSet in the Data Sources Window. Expanding it shows the tables contained in the data set. Expanding a table shows its fields or columns. Visual Studio also generated 4 files grouped as one which is used to created the DataSet. You can see them in the Solution Explorer. They contain all the codes that create our DataSet. You don’t have to look at them for now.
Showing Table Data Via Drag and Drop
Now is the most exciting part. With our DataSet available in the Data Sources Window, we can simply drag a table to the form. You can also drag each column to a form but for now, we will drag a whole table to the form.
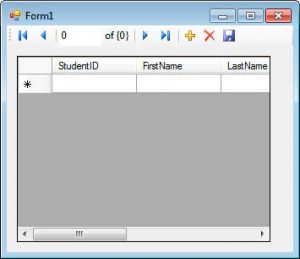
After dragging the table into the form, Visual Studio will automatically create a DataGridView control. The DataGridView allows you to view different kinds of data that can be represented in a table. An example is a database table or a multidimensional array of values. You can see that each column of the Students table was automatically placed in the DataGridView (try to resize the form and the DataGridView to see all the columns). You can also use the Dock property of the DataGridView and set it to Fill so the DataGridView will take up all the space of the form’s client area.
You will a toolbar on the top of the form. It is called the BindingNavigator control and Visual Studio also created this to allow you to move through records, update a record, delete an old record, and add a new record. If you also look at the component try below, more components have been automatically created for you by Visual Studio. We won’t be discussing each of them for now because there are lot’s of concepts to learn first. But if you are to create everything manually, then it can take us a lot of time to create what we have accomplished in this lesson.
Run the application and you will see that all the records are displayed in the DataGridView. You can use the BindingSourceNavigatorcontrol to modify the contents of the database.
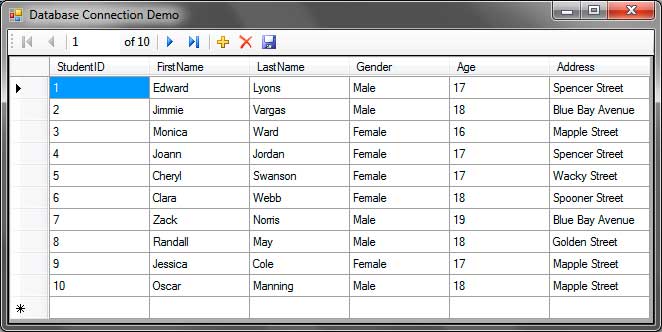
You can use the navigation buttons to move from 1 record to another. The plus icon allows you to add new records. Don’t worry if the StudentID that will be assigned for the new record is a negative number, it will be fixed by clicking the Save button which should be done to save the changes to the database. You can modify each field of a record by double clicking it. You can also delete a selected record by clicking the red X icon in the BindingNavigator control. Again, press the Save button after you have made a change to send the changes to the database.
Note that running your program duplicates the database from the root project folder to the Release or Debug folder so everytime you run your program, you will work with a fresh copy of the database. It implies any adjustment to the database you make will be overwritten and disposed of whenever you run your applicationThis is great when you are simply building up the application. If you don’t want this behavior, select the database file (University.mdf) in the Solution Explorer and in the find the Copy To Output Directory option in the Properties Window. Change its value to Copy if newer. The information go in the project’s root directory can currently solely be coppied if it a more moderen version of the one that already exists within the output directory.